Heritage formats
In the past, market research software has often stored data in proprietary, nonstandard formats that were inaccessible to other consumer applications. For example, IBM SPSS Statistics saves data in .sav files; Quancept data-gathering applications write survey data as text .drs or .dat (case data) and .qdi (metadata) text files; Quantum uses the .dat file in data analysis, whereas Quanvert uses a “flipped” version of the data that is stored in a proprietary database; In2quest writes data to .i2d files, and Surveycraft writes to .qdt and .vq files. This disparity in file types means that data in one format might be inaccessible to other applications.
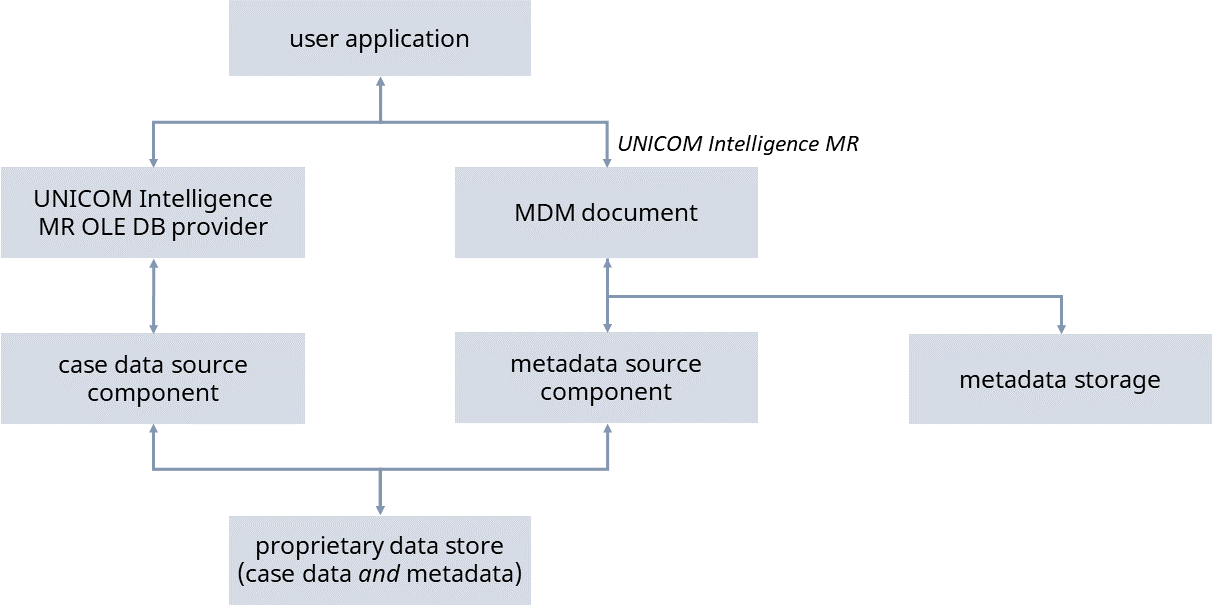
Because the Provider interrogates the CDSC rather than the data store, you can create a new CDSC that allows you to use data that is stored in a different format. Just as the CDSC gives the Provider access to the data store, you can create an MDSC to give the MDM access to the metadata in the data store when there is no metadata stored in an .mdd file. Depending on how the proprietary data is structured, this might be the same data source as that read by the CDSC.
This means that you can leverage heritage data and continue to use it without converting it to a different format. The UNICOM Intelligence Data Model uses OLE DB and COM interfaces, so you can use existing applications to access your data or create your own applications. You are not bound to one set of analysis tools. You can select data using a query written in SQL syntax and pass it to a spreadsheet or other application. If your project has been created using the UNICOM Intelligence Data Model from the outset, you need only one data source component, because all of the project metadata is already stored in .mdd format, which is immediately accessible to the UNICOM Intelligence Data Model. If you are using the UNICOM Intelligence Data Model to access data for which the metadata is stored in a different format, you must use an MDSC that reads metadata from your data files and presents it to the MDM in a form that it can handle. In other words, the UNICOM Intelligence Data Model is open at both ends: to old and new data sources, and to any industry-standard OLE DB analysis tools.
Overview of the UNICOM Intelligence Data Model when using third-party applications and proprietary data storage
See also