|
Unit
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
JOIN UNIT*
|
Join unit joins two or more tables. The join can be done by using loop join or merge join.
|
|
TABLE UNIT
|
The table unit is used to fetch the data rows from a table or index.
|
|
ORDER UNIT
|
Order unit is used to order rows for grouping or to satisfy ORDER BY. The ordering can be done in memory or using an external disk sorter.
|
|
GROUP UNIT
|
Group unit is used to do grouping and aggregate calculation (SUM, MIN, and so on).
|
|
UNION UNIT*
|
Union unit performs the UNION operation. The unit can be done by using loop join or merge join.
|
|
INTERSECT UNIT*
|
Intersect unit performs the INTERSECT operation. The unit can be done by using loop join or merge join.
|
|
EXCEPT UNIT*
|
Except unit performs the EXCEPT operation. The unit can be done by using loop join or merge join.
|
|
Column name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
ID
|
The output row number, used only to guarantee that the rows are unique.
|
|
UNIT_ID
|
This is the internal unit id in the SQL interpreter. Each unit has a different id. The unit id is a sparse sequence of numbers, because the SQL interpreter generates unit ids also for those units that are removed during the optimization phase. If more than one row has the same unit id it means that those rows belong to the same unit. For formatting reasons the info from one unit may be divided into several different rows.
|
|
PAR_ID
|
Parent unit id for the unit. The parent id number refers to the id in the UNIT_ID column.
|
|
JOIN_PATH
|
For join, union, intersect, and except units there is a join path which specifies which tables are joined in the unit and the join order for tables. The join path number refers to the unit id in the UNIT_ID column. It means that the input to the unit comes from that unit. The order in which the tables are joined is the order in which the join path is listed. The first listed table is the outermost table in a loop join.
|
|
UNIT_TYPE
|
Unit type is the execution graph unit type.
|
|
INFO
|
Info column is reserved for additional information. It may contain, for example, index usage, the database table name and constraints used in solidDB® to select rows. Note that the constraints listed here may not match those constraints given in the SQL statement.
|
|
Unit type
|
Text in Info column
|
Description
|
|---|---|---|
|
TABLE UNIT
|
tablename
|
The table unit refers to table tablename.
|
|
TABLE UNIT
|
constraints
|
The constraints that are passed to the database engine are listed. If for example in joins the constraint value is not known in advance, the constraint value is displayed as NULL.
|
|
TABLE UNIT
|
SCAN TABLE
|
Full table scan is used to search for rows.
|
|
TABLE UNIT
|
SCAN indexname
|
Index indexname is used to search for rows. If all selected columns are found from an index, sometimes it is faster to scan the index instead of the entire table because the index has fewer disk blocks.
|
|
TABLE UNIT
|
PRIMARY KEY
|
The primary key is used to search rows. This differs from SCAN in that the whole table is not scanned because there is a limiting constraint to the primary key attributes.
|
|
TABLE UNIT
|
INDEX indexname
|
Index indexname is used to search for rows. For every matching index row, the actual data row is fetched separately.
|
|
TABLE UNIT
|
INDEX ONLY indexname
|
Index indexname is used to search for rows. All selected columns are in the index, so the actual data rows are not fetched separately by reading from the table.
|
|
JOIN UNIT
|
MERGE JOIN
|
Merge join is used to join the tables.
|
|
JOIN UNIT
|
3-MERGE JOIN
|
A 3-merge join is used to merge the tables.
|
|
JOIN UNIT
|
LOOP JOIN
|
Loop join is used to join the tables.
|
|
ORDER UNIT
|
NO ORDERING REQUIRED
|
No ordering is required, the rows are retrieved in correct order from solidDB®.
|
|
ORDER UNIT
|
EXTERNAL SORT
|
External sorter is used to sort the rows.
|
|
ORDER UNIT
|
FIELD n USED AS PARTIAL ORDER
|
For distinct result sets, an internal sorter (in-memory sorter) is used for sorting and the rows retrieved from solidDB® are partially sorted with column number n. The partial ordering helps the internal sorter avoid multiple passes over the data.
|
|
ORDER UNIT
|
n FIELDS USED FOR PARTIAL SORT
|
An internal sorter (in-memory sorter) is used for sorting and the rows retrieved from solidDB® are partially sorted with n fields. The partial ordering helps the internal sorter to avoid multiple passes over the data.
|
|
ORDER UNIT
|
NO PARTIAL SORT
|
Internal sorter is used for sorting. The rows are retrieved in random order from solidDB® to the sorter.
|
|
UNION UNIT
|
MERGE JOIN
|
Merge join is used to join the tables.
|
|
UNION UNIT
|
3-MERGE JOIN
|
A 3-merge join is used to merge the tables.
|
|
UNION UNIT
|
LOOP JOIN
|
Loop join is used to join the tables.
|
|
INTERSECT UNIT
|
MERGE JOIN
|
Merge join is used to join the tables.
|
|
INTERSECT UNIT
|
3-MERGE JOIN
|
A 3-merge join is used to merge the tables.
|
|
INTERSECT UNIT
|
LOOP JOIN
|
Loop join is used to join the tables.
|
|
EXCEPT UNIT
|
MERGE JOIN
|
Merge join is used to join the tables.
|
|
EXCEPT UNIT
|
3-MERGE JOIN
|
A 3-merge join is used to merge the tables.
|
|
EXCEPT UNIT
|
LOOP JOIN
|
Loop join is used to join the tables.
|
|
ID
|
UNIT_ID
|
PAR_ID
|
JOIN_PATH
|
UNIT_TYPE
|
INFO
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
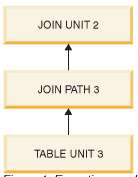
1
|
2
|
1
|
3
|
JOIN UNIT
|
|
|
2
|
3
|
2
|
0
|
TABLE UNIT
|
TENKTUP1
|
|
3
|
3
|
2
|
0
|
|
FULL SCAN
|
|
4
|
3
|
2
|
0
|
|
UNIQUE2_NI <= 99
|
|
5
|
3
|
2
|
0
|
|
UNIQUE2_NI >= 0
|
|
6
|
3
|
2
|
0
|
|
|

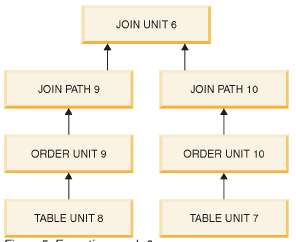
ID | UNIT_ID | PAR_ID | JOIN_PATH | UNIT_TYPE | INFO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | 6 | 1 | 9 | JOIN UNIT | MERGE JOIN |
2 | 6 | 1 | 10 | ||
3 | 9 | 6 | 0 | ORDER UNIT | NO ORDERING REQUIRED |
4 | 8 | 9 | 0 | TABLE UNIT | TENKTUP2 |
5 | 8 | 9 | 0 | PRIMARY KEY | |
6 | 8 | 9 | 0 | UNIQUE2 < 4500 | |
7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | UNIQUE2 > 4000 | |
8 | 8 | 9 | 0 | ||
9 | 10 | 6 | 0 | ORDER UNIT | NO ORDERING REQUIRED |
10 | 7 | 10 | 0 | TABLE UNIT | TENKTUP1 |
11 | 7 | 10 | 0 | PRIMARY KEY | |
12 | 7 | 10 | 0 | UNIQUE2 < 4500 | |
13 | 7 | 10 | 0 | UNIQUE2 > 4000 | |
14 | 7 | 10 | 0 |