Maintaining databases
Carry out regular maintenance of your databases to make sure that they perform well and can be recovered in the event of a system failure:
▪Check the integrity of a database to make sure that data has not been corrupted by a system error.
▪Reorganize or rebuild indexes to improve performance. This is particularly important for projects that are running large numbers of interviews.
▪Release unused disk space.
▪Back up a database.
If you are using the simple database recovery model, the SQL transaction logs are truncated automatically. If you are using a different recovery model, you might need to truncate or delete the SQL transaction logs manually: see
Deleting or truncating log files.
In Microsoft SQL Server, you can set up maintenance tasks that run according to a schedule. The easiest way to do this is to use the Maintenance Plan Wizard.
This section includes instructions for using the wizards to reorganize the indexes of your project databases. For more information about the wizards or maintenance tasks in general, see the SQL Server Books Online documentation.
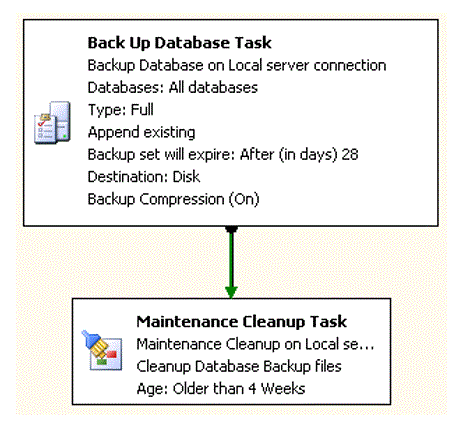
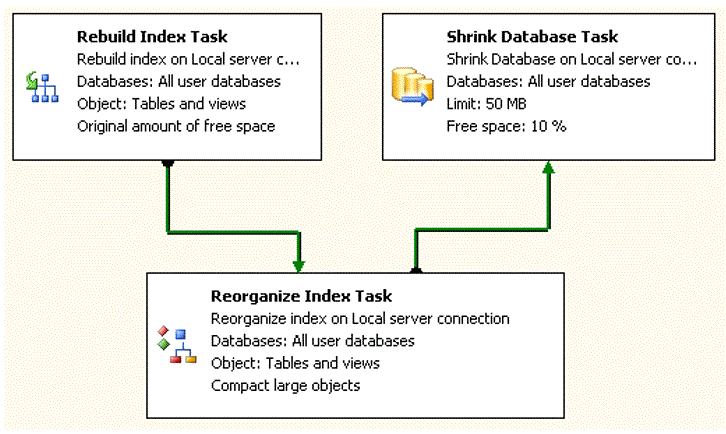
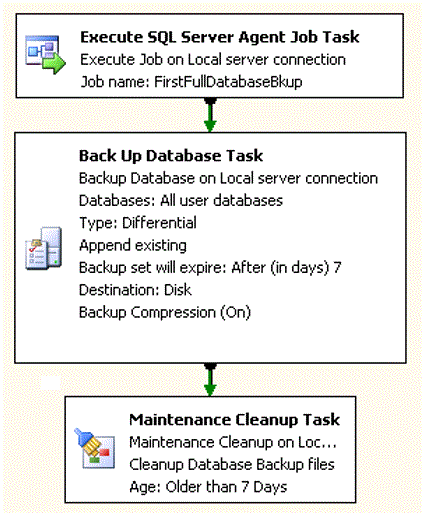
Example maintenance plan
This is an example of a maintenance plan.
When your maintenance plan is in place, ensure that you can restore from your database backups.
Weekly full backup
Weekly database compress
Daily differential backup
See
See also